Understanding Blockchain
A Decentralized Digital Network
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a digital network of computers that work together to maintain a shared record of information. Instead of storing data in one place, like a traditional database, blockchain spreads it across many computers (called nodes). Each node has a complete copy of all records, making the system decentralized - meaning no single person or organization controls it.
First
Next
Latest
Each block connects to form an unbreakable chain
Understanding Blocks
Let's break it down simply:
• Blocks are like containers that hold information - they store things like who sent money to whom, or any other important data
• Once information is put in a block, it can't be changed - it's like writing in permanent marker instead of pencil
How the Network Works
Think of the blockchain network like a neighborhood watch group:
• Instead of one person keeping records, everyone in the network has their own copy (like each neighbor watching their street)
• Before anything new is added, everyone in the network must check and agree it's correct (like neighbors voting on community decisions)
Why It's Secure
The blockchain stays safe because:
• Every piece of information gets a unique fingerprint - if someone tries to change the information, the fingerprint won't match anymore
• Once information is recorded, it's permanent - like carving something in stone
Starting a Transaction
Just like writing a letter, you need to:
• Write down who's sending (that's you!)
• Add who's receiving (your friend)
• Include what you're sending (like $50)
• Package it all together, ready to send
Checking Everything
Before your transaction is accepted:
• The network checks your digital signature - like verifying your fingerprint to prove it's really you
• Special programs (smart contracts) run to make sure all transaction rules are followed
• Just like checking your bank balance, the network verifies you have enough to send
• Every computer in the network does these checks independently
• If anything doesn't match up, the transaction is rejected - keeping everyone's money safe
Making it Official
Your transaction gets locked in:
• Added to a new block with other transactions
• Connected to all previous blocks
• Sealed so it can't be changed
• Like adding a page to a book that can't be torn out
Spreading the Word
The final step:
• Your transaction waits in line with others (like waiting in a queue at a store)
• Special computers (miners) pick which transactions to process next
• After processing, they share the new updates with other computers
• Each computer checks the updates are correct before adding them
• Like a game of telephone, but every computer double-checks the message is right
Blockchain Process
Understanding How Blockchain Works
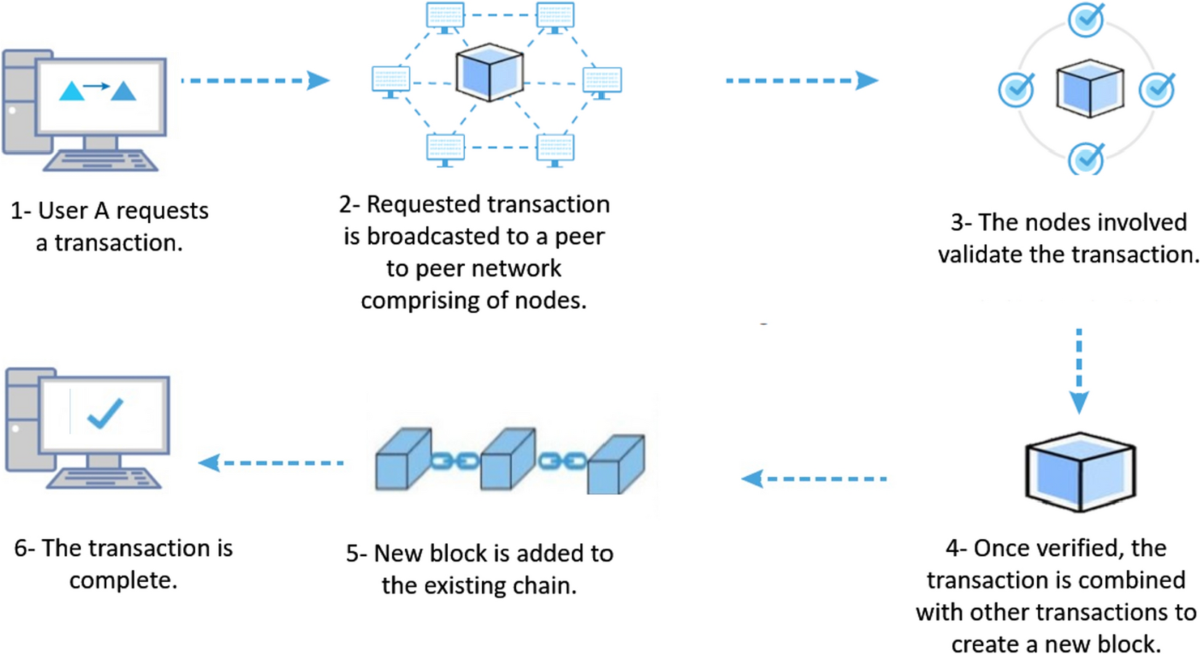
Image source: Springer Nature - Blockchain Technology Illustration
Understanding Blockchain
Think of blockchain like a chain of digital containers: each container (block) holds information that can't be changed - it's like writing in permanent marker instead of pencil, creating a super-secure digital ledger that everyone can trust.
Blockchain Applications
Real-World Uses of Blockchain Technology
Banking & Money
Making money matters simpler and safer:
- Send Money Worldwide: Transfer money internationally in minutes, not days
- Easier Business Deals: Buy and sell internationally with less paperwork
- Quick Insurance Claims: Get your insurance claims processed faster
- Prove Who You Are Online: Secure digital ID that protects your privacy
- Get Loans Faster: Quick loan decisions without endless paperwork
Apps
New ways to use your phone and computer:
- Better Social Media: Own your posts and data, not the big tech companies
- Fun Gaming: Own your in-game items for real
- Safe File Storage: Store files where no one can delete them
Healthcare
Making healthcare more efficient and secure:
- Your Medical History: Access your health records anywhere, anytime
- Real Medicine Checker: Make sure your medicines aren't fake
- Better Medical Research: Help scientists track their studies accurately
- Secure Health Data: Keep your medical information private
- Faster Insurance: Get your medical bills covered quicker
Government Services
Making public services more trustworthy:
- Safe Online Voting: Vote from home securely
- Property Records: Keep track of who owns what without paperwork
- Simple Tax Systems: Make taxes clearer and easier
- Digital ID Cards: Prove who you are online safely
- Public Information: Access government records easily
Shopping & Retail
Making shopping better and safer:
- Spot Fake Products: Know if something is real or counterfeit
- Know Your Product's Journey: See where your purchases come from
- Protect Your Shopping Data: Keep your shopping habits private
- Easy Payments: Pay securely without a credit card
Education & Learning
Making education more accessible and verifiable:
- Prove Your Degree: Share your diplomas digitally
- Share Research Safely: Keep research data secure and accessible
- Digital Report Cards: Keep all your grades in one safe place
- Protected Learning Materials: Access textbooks and courses fairly
Business & Enterprise
How businesses are making work easier and safer:
- Track Products from Factory to Store: Know exactly where your products come from and where they've been
- Keep Track of Company Assets: Like a digital inventory system that can't be tampered with
- Automatic Business Agreements: Contracts that execute automatically when conditions are met
- Verify Product Quality: Ensure products meet standards at every step
- Smart Inventory Control: Never run out of stock or order too much